A lump is a localized area of skin that swells and rises up. It can be hard and rigid or soft and moveable depending on the cause of the lump. The moment a lump starts to appear on the skin, people worry that it may be life-threatening. However, most lumps are benign and non-cancerous. But in some cases, skin lumps can also be dangerous and interfere with daily life.
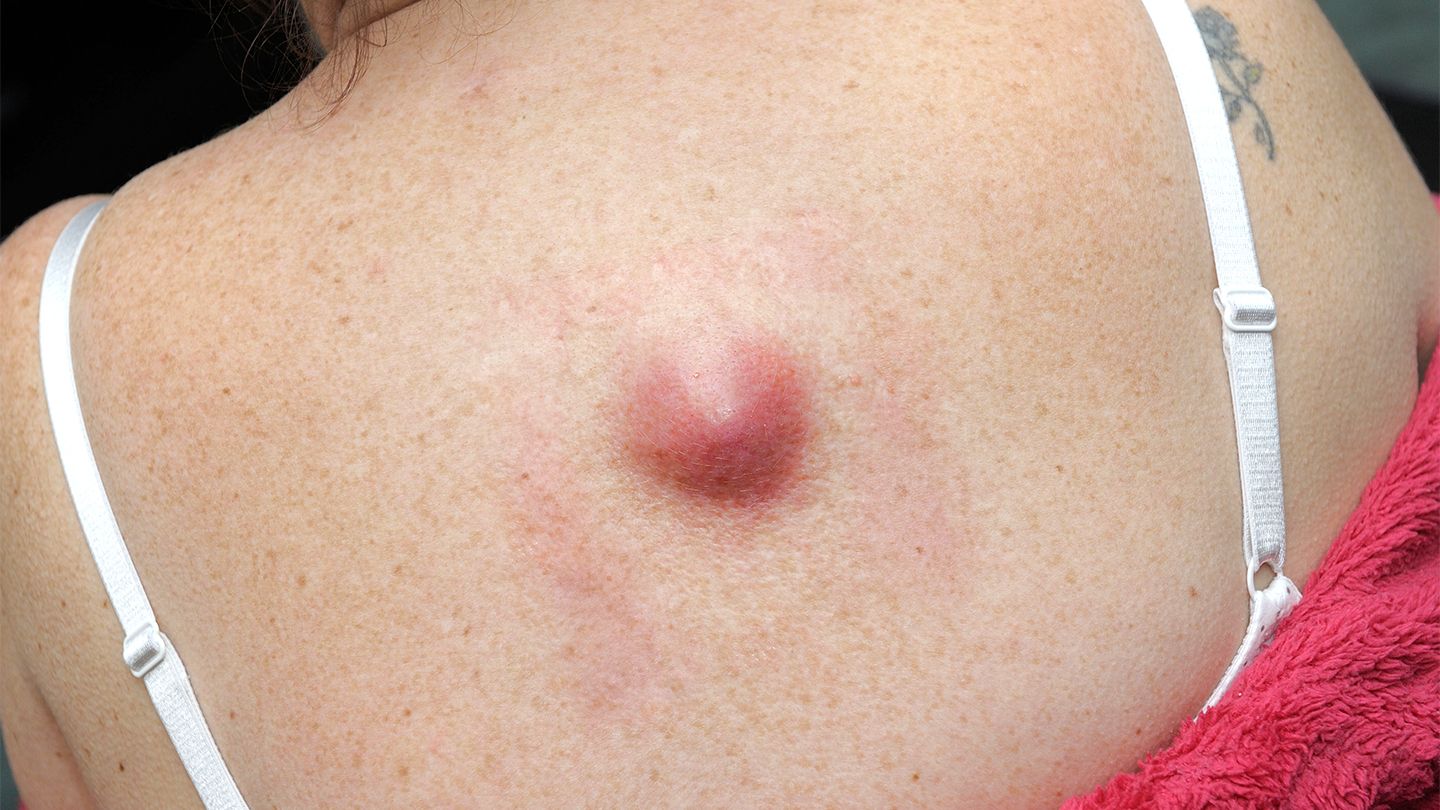

The most common type of lump that people have to deal with is lipoma which appears under the skin. You can contact a daycare provider like Pristyn Care to undergo lipoma surgery and get the condition treated permanently.
Whether you have a small or big lump, hard or soft, you should get in touch with a dermatologist or a plastic surgeon to get diagnosed properly. Today, we will cover what causes lumps and what are the basic differences between cancerous and non-cancerous lumps.
What can cause lumps?
Lumps are tumors that resemble swollen skin. They can be caused due to infection, inflammation, inflammatory diseases, benign cysts, tumors, cancers, and trauma. Mostly, they are temporary and subside as the underlying condition resolves. In other cases, lumps can persist and continue to grow over time indicating that there is a more serious condition to deal with. Here is a list of various causes of lumps:
Traumatic Causes
Some minor or severe injury or internal trauma can cause swelling or lump, such as:
- Broken bones
- Head injury
- Hematoma
- Hernias
- Sting or bite
Infectious Causes
Some infectious diseases can also cause the formation of lumps in different parts of the body. The diseases include:
- Abscesses
- Boils
- Herpes virus infection
- Mononucleosis
- Mumps
- Warts
- Upper respiratory virus infection, including cold.
Inflammatory Causes
Some conditions that cause inflammation in the body also produce lumps. These conditions are:
- Gout
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatic Fever
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Tumors That Causes Lumps
Both cancerous and non-cancerous tumors cause lumps to appear on the skin:
- Breast cancer
- Breast cyst
- Fibroma (benign)
- Lipoma (benign)
- Lymphoma (cancerous)
- Melanoma (cancerous)
- Nevi (moles of the skin)
- Non-melanoma skin cancers
- Thyroid cancer
- Brain hemorrhage
- Cancer
Among all these conditions that cause lumps, most can be resolved with home care and prescription medications. But some cancerous tumors need surgical and further treatment. The best thing to do is to consult a specialist the moment you notice the lump. Even if you know some basic differences between a cancerous and non-cancerous lump, it is necessary that you get it diagnosed by an expert and explore your treatment options.
How to differentiate between a cancerous and non-cancerous lump?
The occurrence of lump is usually associated with additional symptoms depending on the underlying disease, condition, or disorder. Sometimes, localized symptoms may be present, such as pus or discharge, redness, tenderness, or pain with the lump. Some other body system-related symptoms can also be noticed with lumps, including:
- Cough, fever, and chills
- Headache and nervousness
- Joint stiffness and pain
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
- Runny nose and sore throat
- Sweating and unexpected weight loss
The above-mentioned symptoms are a sign that the tumor or lump is non-cancerous and caused due to some other conditions.
However, if the following symptoms are present with the lump, it means that you need to be wary and seek immediate care.
- Changes in consciousness or alertness, e.g. passing out or unresponsiveness.
- Sudden behavior change or abnormal mental state resulting in confusion, delirium, lethargy, hallucinations, and delusions.
- Uncontrollable bleeding.
Apart from these symptoms, you can differentiate between a cancerous and non-cancerous tumor by looking for the following characteristics.
| Characteristics of Non-cancerous Lumps | Characteristics of Cancerous Lumps |
| The tumor grows slowly | The tumor grows rapidly |
| Doesn’t spread to other muscles or organs | Can spread to other muscles and organs |
| Do not invade nearby tissues | Invade the basal membrane that surrounds the nearby tissues |
| Have clear boundaries | May spread via bloodstream or lymphatic system |
| The shape, chromosomes, and DNA of the tumor appear normal under the microscope | The cancerous tumor has abnormal chromosomes and DNA characterized by dark and large nuclei that have an abnormal shape |
| No secretion of hormones or other substances | Can secrete substances that cause weight loss and fatigue |
| Can be left untreated if there is no threat of life | Require immediate treatment as they are life-threatening |
| Unlikely to recur after removal | May recur after removal, sometimes in other locations |
| Doesn’t require radiation or chemotherapy for treatment | Treatment is primarily done through radiation, chemotherapy, and, immunotherapy medications. |
How to treat lumps?
The treatment of lumps depends on their cause. For instance, a lump that is caused by lymph node swelling, enlarged salivary glands, skin rash, or viral illness can be managed and treated by home care methods, such as using icepacks, baking soda baths, fever-reducing medications, etc. The lumps caused by injuries resolve as the body starts to heal.
If the infection is caused due to infection or abscess, then you are most likely to need antibiotic medications to fix the lump. Topical medications can eliminate lumps caused by acne, warts, or rashes. For inflamed lumps, skin infections, and benign cysts, corticosteroid injections can be used for treatment.
For a lump that keeps growing in size and causes pain, the best treatment is surgery. Some common lumps, both cancerous and non-cancerous that require surgical treatment are cysts, lipoma, abscesses, fibroma, hemangiomas, etc.
You should never delay getting treatment for a lump as there are few causes of lumps that can be misdiagnosed. Due to this, there are chances that a cancerous lump goes unnoticed for a long time and become fatal over time.
Can a benign lump/tumor turn into cancer?
Most types of benign lumps do not transform into cancer. However, some types, such as adenomas do have a greater risk of turning into cancer. It is often hard to tell whether a lump is cancerous or not by merely looking at it. That’s why it is critical that you get diagnosed properly. If the doctor suspects that the lump is cancerous, a biopsy will be performed for confirmation.
Depending on the diagnostic test results, the doctor will suggest the most appropriate treatment method for you.
The Bottom Line
We understand that a lump appearing out of nowhere can be alarming. But you need to be attentive too. If a lump appears on any part of your skin, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible and rule out the possibility of cancer.
